15
2022
-
12
Gradient cemented carbide matrix
Author:
STREAMARY
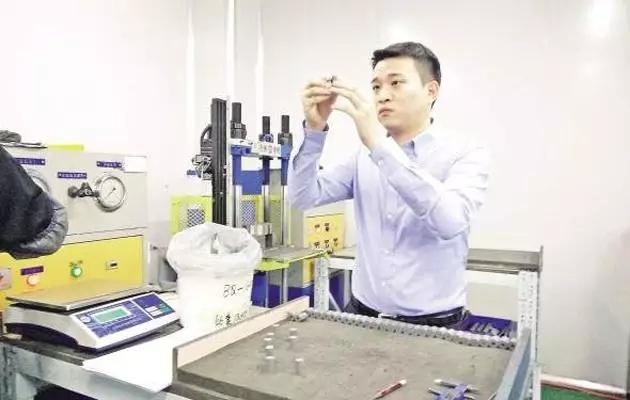
As a tool material, cemented carbide has been widely used in various cutting tools, mining tools and wear-resistant and corrosion-resistant parts due to its high hardness, high strength, high elastic modulus, wear resistance and corrosion resistance.
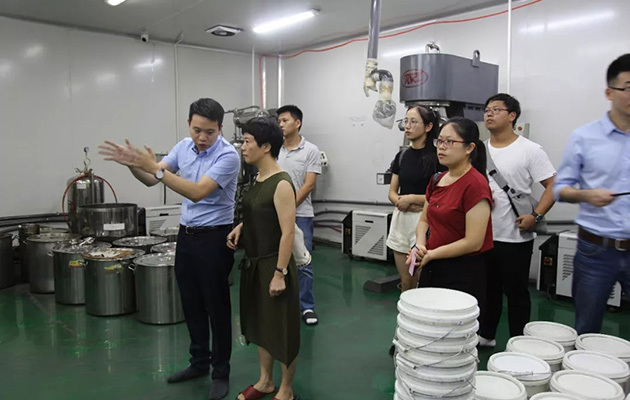
As a tool material, cemented carbide has been widely used in various cutting tools, mining tools and wear-resistant and corrosion-resistant parts due to its high hardness, high strength, high elastic modulus, wear resistance and corrosion resistance. In order to adapt to various service conditions and improve service efficiency, in view of the contradiction between high hardness and low toughness of traditional cemented carbide, people have developed materials such as gradient cemented carbide and ultra-fine cemented carbide.
In recent years, with the introduction of the concept of functionally graded materials, functionally graded cemented carbide is developing into one of the important research contents in the field of cemented carbide. In order to improve the cutting performance and service life of cemented carbide cutting tools, a thin layer of high hardness wear-resistant material can be coated on the surface of the alloy. Due to the different thermal expansion coefficients of different materials, the coating materials may crack due to thermal stress during cooling.
Because of the brittleness of the coating material, cracks are more likely to occur on the surface of the coating and spread to the substrate. In order to prevent the material failure caused by crack propagation as much as possible, and to facilitate the acquisition of high performance cemented carbide cutting tool materials, the matrix can be subject to gradient treatment to form a tough area lacking cubic carbide and carbonitride on the surface of the matrix. The binder content in this area is higher than the nominal binder content of the matrix.
When the crack formed in the coating extends to this area, due to its good toughness, it can absorb the energy of crack propagation, thus effectively preventing the crack from extending to the inside of the alloy and improving the service performance of cemented carbide cutting tools.